On October 16, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology officially released the "Catalogue of Technologies and Products Encouraged for Promotion and Application in the Building Materials Industry (2025 Edition)."
This initiative aims to promote the widespread application of new technologies and products in the building materials industry, direct resources toward emerging industries and technological transformation of traditional industries, and accelerate the industry's transformation toward high-end, intelligent, and green development.
Amid this transformation, building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), as a key vehicle for empowering buildings with "productivity," are becoming increasingly strategically important. The most important applications for BIPV are curtain walls and skylights, which are the primary applications for thin-film photovoltaic modules, and cadmium telluride (CTE) is a must-have.
Notably, thin-film photovoltaic modules for architectural applications, such as CdTe and Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS), are also included in this catalogue for promotion.
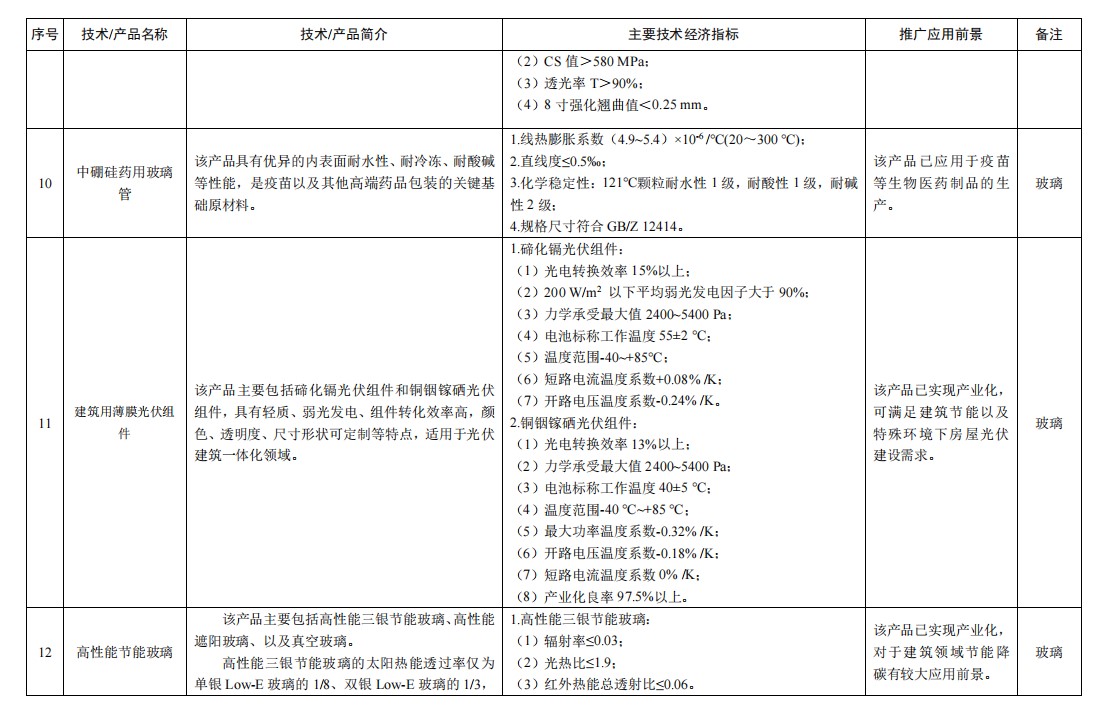
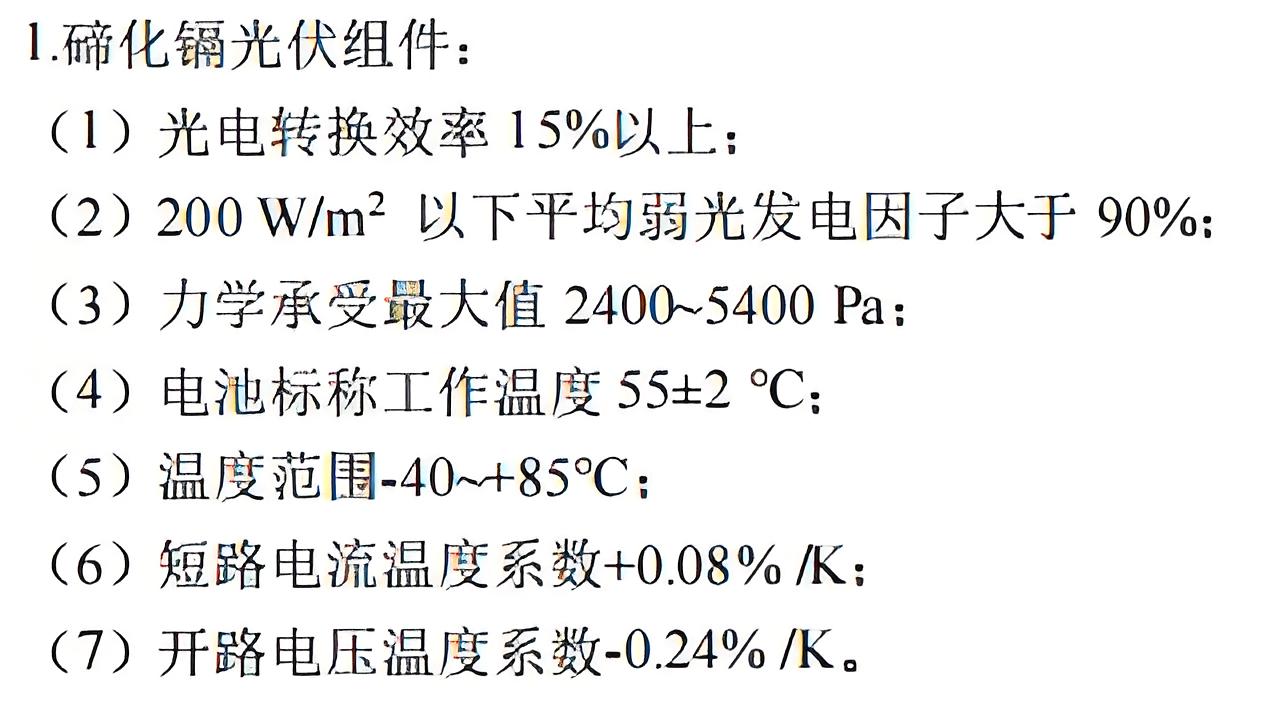
Core Advantages of CdTe
CdTe is typically grown directly on glass substrates using three thin-film deposition techniques: vapor transfer deposition (VTD), near-space sublimation, or modified near-space sublimation. Thin films only 1-3 microns thick are grown directly on glass substrates. Its core power generation occurs at the p/n junction interface. More importantly, cadmium telluride is a direct-bandgap semiconductor. Its 1.45eV bandgap perfectly matches the solar spectrum, efficiently converting photons into electrons.
1. Technical DNA
Outstanding Low-Light Power Generation Capability
As a direct-band gap material, cadmium telluride (CdTe) absorbs the entire spectrum well. Its power generation performance significantly outperforms crystalline silicon (CdTe), an indirect-bandgap material, in low-light conditions such as early morning and evening, dust accumulation, and haze, providing a solid foundation for capturing high-priced electricity.
High Oblique Light Capture Efficiency
Thanks to its superior incident angle response (lower IAM losses), CdTe modules can more effectively reduce reflections and absorb more oblique light during the morning and evening hours when the sun's angle is low, generating more power under the same lighting conditions.
Resistant to shading and no hot spot effects
CdTe's thin film structure is inherently resistant to shading. First, the single-cell area is large (up to 3 square meters) and the number of internal series-connected cells is small. Second, the thin-film material itself has better heat resistance. Relevant tests show that under the same shading conditions, the power loss of cadmium telluride is only one-third that of crystalline silicon, and destructive hot spots are virtually nonexistent.

2. New Value Narrative
Precisely Matching the Market Curve
The unique feature of cadmium telluride thin-film modules, with higher output in the morning and evening, perfectly aligns with the fluctuating electricity market curve, where electricity prices are higher in the morning and evening, and lower at noon.
Flexible Application Scenarios
As thin-film modules, they offer a uniform and beautiful appearance and are easily integrated with building facades and rooftops (BIPV).
Green Cycle Carbon Reduction
With a short energy payback period and low energy consumption during production, they contribute to carbon reduction throughout their lifecycle.
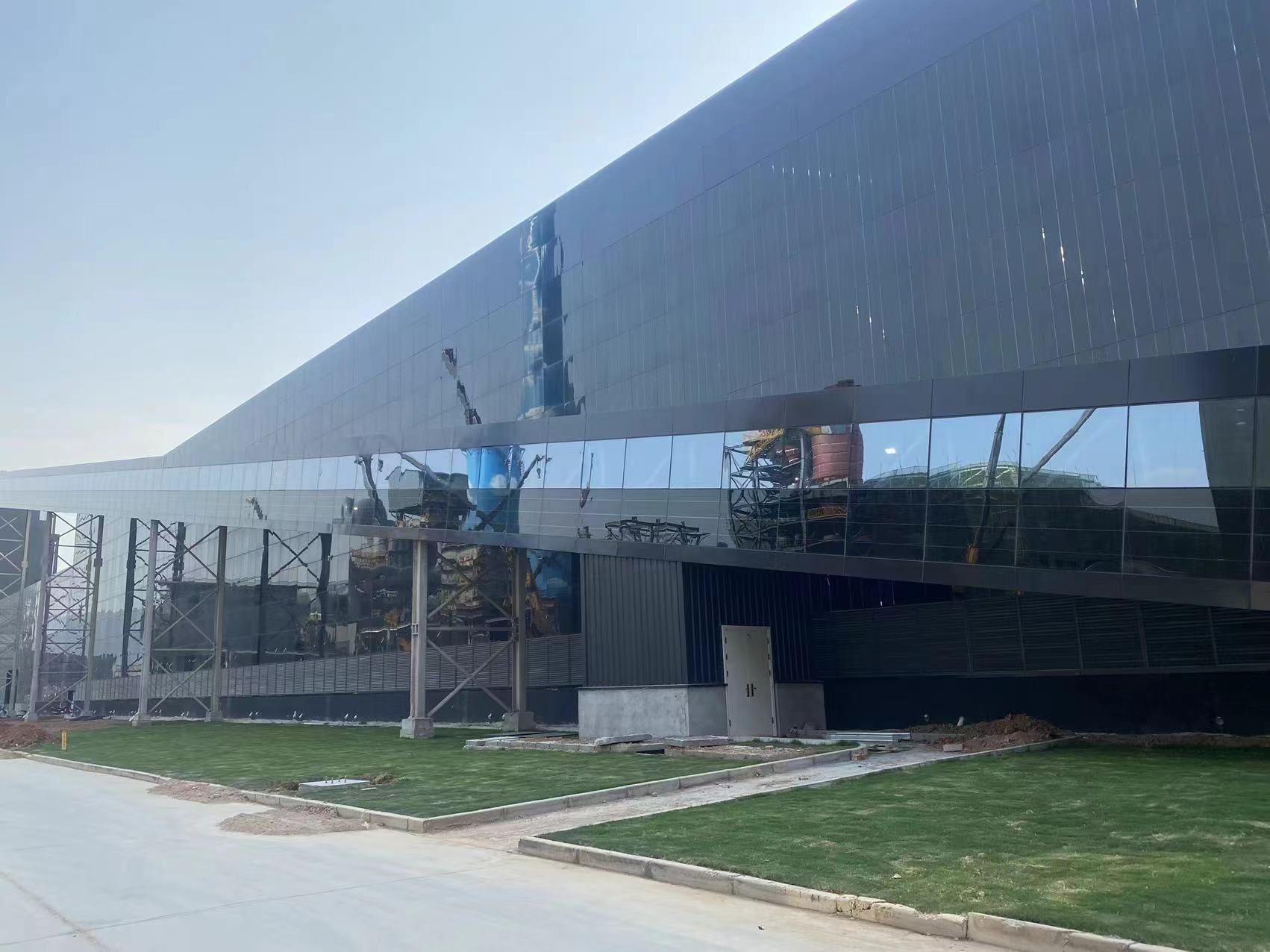

Overall, cadmium telluride thin-film photovoltaic modules are undoubtedly a highly competitive technology with great development potential in the BIPV market. They are particularly likely to become a mainstream choice in the aesthetically pleasing BIPV sector.
As an active promoter in this field, ZOOM SOLAR Green Energy Technology is relying on its accumulation in cadmium telluride technology research and development and product innovation, and is committed to providing customers with high-performance, high-reliability and highly customized BIPV solutions, contributing professional strength to the green and low-carbon transformation of buildings.