The sun is the primary energy source for life as we know it, and it is also the largest and most direct energy source. It's estimated that the 4.3 million kilowatts of sunlight reaching Earth in one hour is more than the 4.1 million kilowatts of energy consumed by Earth in a year. Against the backdrop of global warming and the depletion of fossil fuels, vigorously developing renewable energy has become a global consensus. As an environmentally friendly and sustainable energy supply, solar cells are becoming a core force in transforming the energy landscape.

Cadmium telluride thin-film solar cells are the second most common photovoltaic (PV) technology after crystalline silicon. They feature low degradation, light weight, low cost, high efficiency, stable performance, easy scalability, low energy consumption, and suitability for building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). They are the first of the second-generation thin-film PV technologies to achieve large-scale commercial deployment.

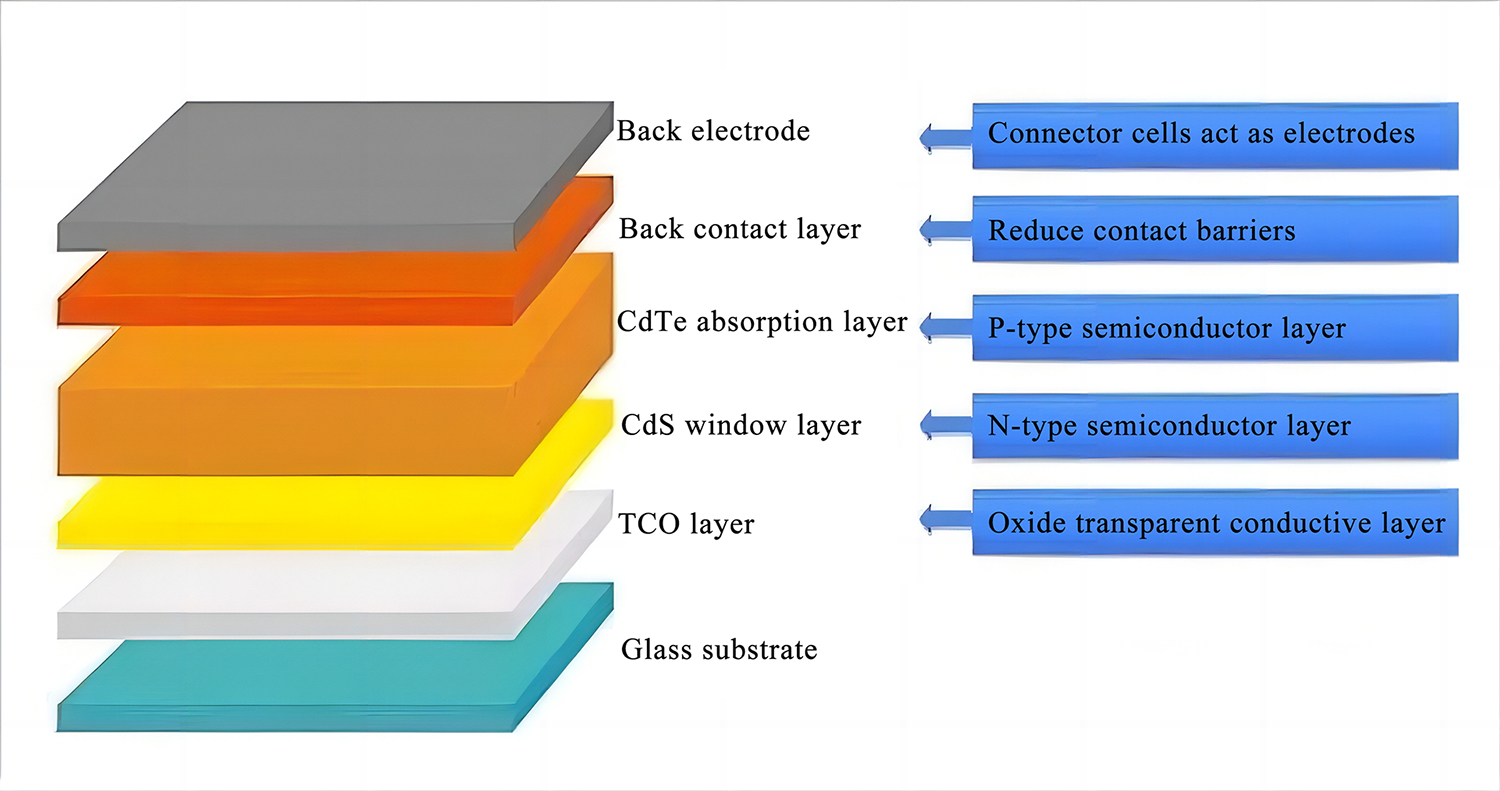
In terms of product structure, cadmium telluride thin-film solar cells typically consist of a glass substrate, a transparent conductive oxide (TCO), an n-type cadmium sulfide (CdS) window layer, a p-type cadmium telluride (CdTe) absorber layer, a back contact layer, and a back electrode layer. When sunlight penetrates the glass substrate and various functional layers, photon energy is efficiently captured in the CdTe absorber layer, generating electron-hole pairs. Subsequently, under the action of an internal electric field, the electrons and holes migrate in a directional manner, ultimately forming an electric current and initiating the remarkable transformation of light into electricity.
In practical applications, a number of cadmium telluride thin-film monolithic cells are sealed together in series or parallel to form a module for ease of use and installation. In today's era of pursuing green and sustainable energy development, the application scenarios of cadmium telluride thin-film photovoltaic modules are extremely diverse.
1. Architecture: The New Standard for Green Buildings
Cadmium telluride thin-film photovoltaic modules are an ideal choice for modern buildings. It can perfectly replace traditional curtain wall materials, transforming into a "power-generating glass" curtain wall that combines aesthetics with power generation. It not only effectively blocks UV rays and external heat, creating a comfortable indoor environment, but also quietly converts solar energy into electricity. This significantly reduces modern buildings' reliance on traditional power grids, enabling self-sufficiency in building energy consumption and leading cities towards a low-carbon, smart future.

Cadmium telluride thin-film photovoltaic modules also have great potential in residential buildings. They can be used on rooftops, sunrooms, and skylights, providing shelter while harnessing abundant sunlight to generate electricity. This electricity can meet daily household electricity needs, reducing utility bills and allowing residents to truly enjoy the benefits of green energy. Furthermore, excess electricity can be stored to cope with unexpected power outages, ensuring residents' convenience and safety.

2. Industrial and Commercial Sector - Helping Enterprises Transform to Green Energy
Various industrial and commercial parks and factories, as clusters of industries, consume significant energy. Installing cadmium telluride thin-film photovoltaic modules within these parks and factories, as well as on their rooftops, can create a distributed energy system. The vast majority of electricity required for daytime production can be generated by self-generated electricity, significantly reducing the cost of purchasing electricity from the grid and effectively alleviating electricity shortages in industrial and commercial sectors. Excess electricity can also be sold to the grid, generating additional revenue. Furthermore, by using clean energy for power generation, businesses enhance their environmental image, gain a competitive advantage in the market, and lay a solid foundation for sustainable development.
3. Transportation Sector - Pioneering Green Travel
Photovoltaic carports: Cadmium telluride thin-film photovoltaic carports are becoming increasingly popular in urban parking lots, bus stops, and highway service areas. The photovoltaic modules on the roof of the carports provide shade and rain protection for vehicles while converting solar energy into electricity. This electricity can be used to power lighting, charging stations, and other facilities within the carports, facilitating electric vehicle charging and promoting the widespread use of new energy vehicles. Excess electricity can also be fed into the surrounding power grid, achieving energy recycling.

Traffic Lights and Streetlights: Cadmium telluride thin-film photovoltaic modules provide a reliable off-grid power supply solution for traffic lights and streetlights. These modules eliminate the need for external power cables and operate reliably solely on solar energy. The modules charge during the day and power the lights at night, saving energy and reducing maintenance costs. This ensures the continuous and stable operation of traffic lighting facilities and protects road safety.
4. Agriculture - Empowering Modern Agricultural Development
Cadmium telluride thin-film photovoltaic modules are used on the roofs of modern greenhouses for crop cultivation and livestock farming. Installed on the rooftops, these modules maintain daylighting requirements while converting solar energy into electricity to power irrigation equipment, temperature control systems, and supplemental lighting, enabling automated and intelligent agricultural production. Furthermore, the modules provide a degree of sunshade, preventing excessive summer temperatures in the greenhouses and minimizing heat damage to crops. This ensures a stable growing environment for plants and animals, improves agricultural yield and quality, and contributes to increased agricultural efficiency and farmers' incomes.

Environmental protection and sustainable development are issues that human society must confront and address. Cadmium telluride thin-film photovoltaic products, as a new building energy material, are both highly efficient and green, energy-saving, and energy-generating. They are ideally suited for distributed, modular, and integrated green buildings, and are a key tool in achieving the nation's carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals.
Zoom Solar Green Energy Technology is a high-tech new energy enterprise specializing in the research and development, production, manufacturing, and sales of thin-film solar cell chips. The planned 300MW CdTe thin-film module production line can produce large-scale 2400x1600mm standard cadmium telluride thin-film modules, with a maximum power output of 550W per module and a conversion efficiency of 17%. This is an internationally leading position and represents a new high-quality productive force in China's cultivation of advanced energy materials.